What is Vaccination?
Vaccination is a safe and effective way to protect yourself and your family from infectious and harmful diseases. It works by training your immune system to recognise and respond to harmful germs (viruses or bacteria) without causing the actual disease1.
Simply put, vaccination prepares your body with the defences needed to detect and fight potential threats, ensuring long-term protection against preventable diseases1.
Why Vaccination Matters?
Who Needs Vaccination?
Vaccination is a lifelong commitment to health, ensuring protection against preventable diseases at every stage of life6.
Understanding Diseases: Blogs
-
Chickenpox Prevention in Children: Symptoms and Protection through Varicella Vaccination
12-03-2025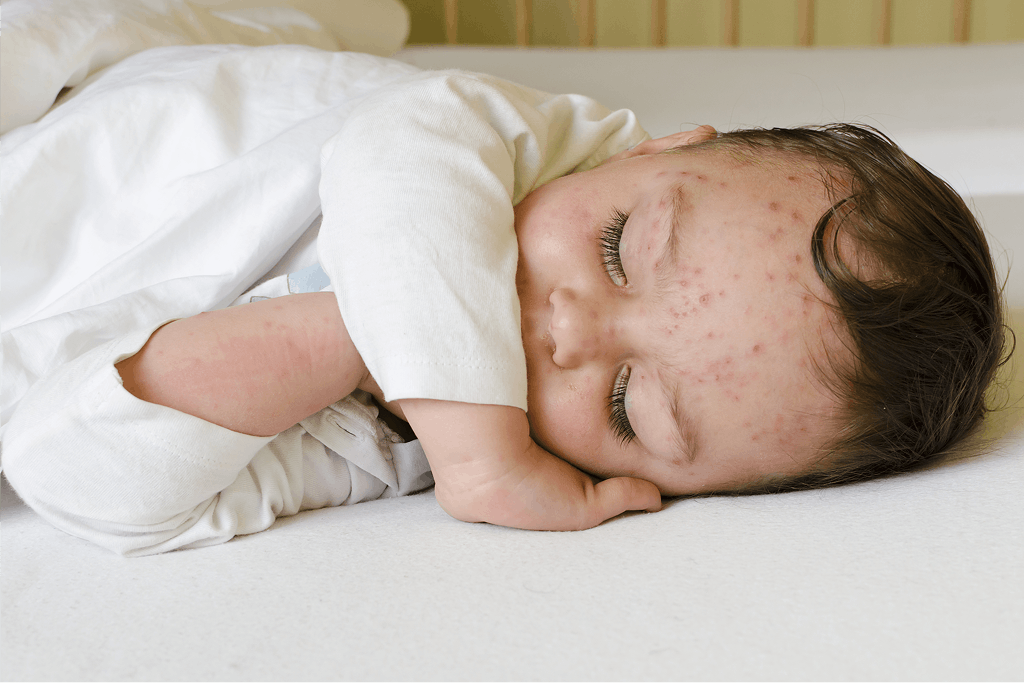 Read more »
Read more »
India Talks Prevention : In The News
-
GSK's new campaign asks parents to support their children's future with 7 crucial vaccinations
25-07-2024 6 min readRead more »
6 min readRead more » -
"Yeh Science Hai": Amitabh Bachchan and Manoj Pahwa partner with GSK for new shingles awareness and prevention campaign
12-08-2024 6 min readRead more »
6 min readRead more »
References
- Vaccines and immunization: What is vaccination? (n.d.). Who.int. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/vaccines-and-immunization-what-is-vaccination
- Vaccines and immunization. (n.d.). Who.int. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.who.int/health-topics/vaccines-and-immunization
- 10 reasons to get vaccinated. (n.d.). Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.nfid.org/immunization/10-reasons-to-get-vaccinated/
- (N.d.). Nih.gov. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2739303/#:~:text=Newborns%20have%20an%20immature%20immune,vaccines%20achieve%20high%20population%20penetration
- Who Should not Get Vaccinated. (2025, February 3). Cdc.gov. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/should-not-vacc.html
- CDC. (2024, October 2). Vaccines and the diseases they prevent. Vaccines & Immunizations. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/by-disease/index.html
- CDC. (2024a, August 10). Explaining how vaccines work. Vaccines & Immunizations. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/basics/explaining-how-vaccines-work.html
- CDC. (2024c, October 11). What Vaccines are Recommended for You. Vaccine Information for Adults. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines-adults/recommended-vaccines/index.html
- Vaccinations and older adults. (n.d.). National Institute on Aging. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/immunizations-and-vaccines/vaccinations-and-older-adults
- CDC. (2025, January 31). Why maternal vaccines are important. Pregnancy and Vaccination. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines-pregnancy/hcp/maternal-vaccines/index.html
- Vaccine-preventable diseases. (n.d.). Who.int. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.who.int/teams/immunization-vaccines-and-biologicals/diseases
- HPV vaccination recommendations. (2025, February 10). Cdc.gov. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/hpv/hcp/recommendations.html
- CDC. (2025b, February 10). Recommended vaccinations for adults. Vaccines & Immunizations. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/imz-schedules/adult-easyread.html
- (N.d.-d). Unicef.org. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.unicef.org/parenting/health/parents-frequently-asked-questions-vaccines
- Indian academy of pediatrics (IAP) advisory committee on vaccines and immunization practices (ACVIP): Recommended immunization schedule (2020-21) and update on immunization for children aged 0 through 18 years. (n.d.). Indianpediatrics.net. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.indianpediatrics.net/jan2021/jan-44-53.htm
- Jones, C. E., Danovaro-Holliday, M. C., Mwinnyaa, G., Gacic-Dobo, M., Francis, L., Grevendonk, J., Nedelec, Y., Wallace, A., Sodha, S. V., & Sugerman, C. (2024). Routine Vaccination Coverage — Worldwide, 2023. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 73(43), 978–984. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7343a4
- CDC. (2024a, August 9). Reasons to follow CDC’s recommended immunization schedule. Vaccines for Your Children. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines-children/schedules/reasons-to-follow.html
- Measles. (n.d.). Who.int. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles
- India meets WHO global standards for vaccine regulation. (n.d.). Who.int. Retrieved February 27, 2025, from https://www.who.int/india/news/detail/15-10-2024-india-meets-who-global-standards-for-vaccine-regulation
- CDC. (2024f, December 23). Multiple vaccines at once. Vaccine Safety. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccine-safety/about/multiples.html
- CDC. (2024, October 3). Shingles vaccination. Shingles (Herpes Zoster). https://www.cdc.gov/shingles/vaccines/index.html


.png?auto=format)



